Lab instructions
HPLC
high performance liquid chromatography
1. Preparation of the mobile phase
distilled water: 30%
MeOH : 70%
eluent was prepared: MeOH/H2O (70/30 v/v)
To prepare 500ml eluent: 150ml Water is mixed with 350 MeOh.
there are two ways to prepare eluent:
i) by adding a specific volume of water to a specific volume of MeOH, the final volume will not be equal to summation amount of water and MeOh. This is because during the mixing process, MeOH may evaporate or the ''equal'' density of mixture when it is mixed with different solvent with different density. By mixing this way we can assure that the fraction of water or MeOH in the solvent is accurately desired.
ii) by adding water to a sepcific volume of MeOH untill we get a final volume, this the proportion between water and MeOH will be different from our desired proportion. The reason is the amount of water or MeOH will higher than amount that is necessary to have a mixture.
There also are some factors that effect the mixture process such as the remaining water and MeOH, formation of cluster...
In this experiment we added 150ml water to 350ml MeOH, the procedure for eluent preparation must be properly described in a method, because eluent affects the retention time, in this experiment, if fraction of MeOH increases, the eluent will be more polar as well as uracil, benzene and toluene and the retention times also are decreased.
2. Degassing and filtrating

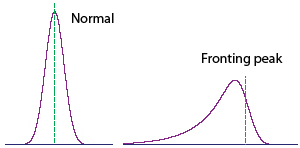
For the peak of toluene, it is fronting. This can be explained as high diffusion coefficient of toluene before coming to the column, and its interactions with stationary phase.(have a look at HPLC troubling here)

HPLC
high performance liquid chromatography
1. Preparation of the mobile phase
distilled water: 30%
MeOH : 70%
eluent was prepared: MeOH/H2O (70/30 v/v)
To prepare 500ml eluent: 150ml Water is mixed with 350 MeOh.
there are two ways to prepare eluent:
i) by adding a specific volume of water to a specific volume of MeOH, the final volume will not be equal to summation amount of water and MeOh. This is because during the mixing process, MeOH may evaporate or the ''equal'' density of mixture when it is mixed with different solvent with different density. By mixing this way we can assure that the fraction of water or MeOH in the solvent is accurately desired.
ii) by adding water to a sepcific volume of MeOH untill we get a final volume, this the proportion between water and MeOH will be different from our desired proportion. The reason is the amount of water or MeOH will higher than amount that is necessary to have a mixture.
There also are some factors that effect the mixture process such as the remaining water and MeOH, formation of cluster...
In this experiment we added 150ml water to 350ml MeOH, the procedure for eluent preparation must be properly described in a method, because eluent affects the retention time, in this experiment, if fraction of MeOH increases, the eluent will be more polar as well as uracil, benzene and toluene and the retention times also are decreased.
2. Degassing and filtrating
In this experiment the filter used is Millipore Durapore.
The eluent is filtered with a 0,45um membrane(hygrophil) the filter procedure was made following:
Turn the pump on, connect the pump to botom, put the filter in, and then after finshing filtering take out the tube and turn off the pump. The particles with the diameters are higher then 0.45um will be kept at membranes, the particles with lower size still pass through the membrance. If the particles are not taken away, they will deteriorate the column, change the column composition. You can find filter manufactures here.


The eluent is filtered with a 0,45um membrane(hygrophil) the filter procedure was made following:
Turn the pump on, connect the pump to botom, put the filter in, and then after finshing filtering take out the tube and turn off the pump. The particles with the diameters are higher then 0.45um will be kept at membranes, the particles with lower size still pass through the membrance. If the particles are not taken away, they will deteriorate the column, change the column composition. You can find filter manufactures here.
The problems of selecting a filter are related to which eluents will be chosen for separation. Filter may release substances to the eluent, or be dissolved by the eluent, so the selected filter should not change the properties of eluent.
The eluent must be purged with nitrogen to take out air bubbles that will have some adversely effects on the detector as well as column efficiency.
- the peaks will be distorted
- formation of oxigen complexation.
3. Sample preparation
Benzen, toluen, and ucal 2000ppm were prepared in the labrotory,
then they are diluted to 20ppm, by taking 30ml sample and add to 2970 water.
We had a sample with 3000ml
The reasons for dilution sample is that if a lot sample come in the detector, the signal will be overloaded, and difficult to relize signals for each component from the sample, as well as its intensity.
4. Instrumentation aspects.
- Column 150*4.6mm(lenght and internal column diameter)packed with 3.5um particle size C18(this type of carbon packing is porous in their stucture)
- The flowrate: 1.2 ml/min, if the flowrate is increased, the pressure also increases, the pump may shut off if the running pressure exceeds the maximum. There is no difference in the baseline noise at 0.8 mL/min and 1.2 mL/min
- Detector: UV-Detectors.
- Pumping: noise pressure caused from the moving of pitton.
5. Baseline setting
Run the system about 15min,
the baseline may be drift due to the inhomogeneous packing column, or mobile phase and stationary phase interactions(MP-STP interactions), contaminants, strong interaction eluent and stationary phase.
Baseline was set with flowrate 0.5ml/min, Pressure 15MPa
6. Inject the sample
The sample is injected by syringe, The injection port has loading and inject manual. the sample is loaded and then injected. Note that you should take the syringe out before turn to inject.
- the loop volumn is 20ul so the wasted sample will come out and the remaing 20ul will be in the loop to be analyzed. The computer software is used to monitor the signal from the detector. After the sample is injected, click "run" at the same time.
The eluent must be purged with nitrogen to take out air bubbles that will have some adversely effects on the detector as well as column efficiency.
- the peaks will be distorted
- formation of oxigen complexation.
3. Sample preparation
Benzen, toluen, and ucal 2000ppm were prepared in the labrotory,
then they are diluted to 20ppm, by taking 30ml sample and add to 2970 water.
We had a sample with 3000ml
The reasons for dilution sample is that if a lot sample come in the detector, the signal will be overloaded, and difficult to relize signals for each component from the sample, as well as its intensity.
4. Instrumentation aspects.
- Column 150*4.6mm(lenght and internal column diameter)packed with 3.5um particle size C18(this type of carbon packing is porous in their stucture)
- The flowrate: 1.2 ml/min, if the flowrate is increased, the pressure also increases, the pump may shut off if the running pressure exceeds the maximum. There is no difference in the baseline noise at 0.8 mL/min and 1.2 mL/min
- Detector: UV-Detectors.
- Pumping: noise pressure caused from the moving of pitton.
5. Baseline setting
Run the system about 15min,
the baseline may be drift due to the inhomogeneous packing column, or mobile phase and stationary phase interactions(MP-STP interactions), contaminants, strong interaction eluent and stationary phase.
Baseline was set with flowrate 0.5ml/min, Pressure 15MPa
6. Inject the sample

The sample is injected by syringe, The injection port has loading and inject manual. the sample is loaded and then injected. Note that you should take the syringe out before turn to inject.
- the loop volumn is 20ul so the wasted sample will come out and the remaing 20ul will be in the loop to be analyzed. The computer software is used to monitor the signal from the detector. After the sample is injected, click "run" at the same time.
Now get started by injecting the sample with
the results

Table 1. the results for uracil, benzene, toluene with different mobile phase flow rates.
Because column is packed with non-polar C18, so the more components are polar the less it will be retained in the column, the polarity is ranged from lowest toluen, benzen, ucal you can see the polarity index here
So the peak appeared following:
the peak 1: uracil
the peak 2: benzen
the peak 3: toluen
and we have plot Van Deemter for column 1 made of Halo
packed with C18, particle size: 3,5um, lenght: 150mm, internal diameter: 4.6mm
the sample containing uracil, benzene, and toluene. Van Deemter is used to determine the efficiency of column, in this case it is used to compare the efficiency of three components.

7. Determination of Void volume
Void volume or dead volume is the amount of eluent filled from the injection port to the point where the detector is placed. If this volume is large, which will lead to band broadening of band during the transportation of sample.
the void volume is determined by injecting NaNO3 that is not retained by the column.
We calculate
V(void volume) = Flowrate* t(when the peak of NaNO3 appears)
6,857min 0,2 mL/min, V = 0,13714 ml
3,513min 0,4 mL/min, V = 0,14052 ml
the difference in void volume when it is determined at different flow rate does not vary sightly.
8. Extra column Band broadening
Extra column band broadening is call longitude diffusion that happens in tubes connected to columns from injection ports, detector to column.
To have a general knowledge about extra column band broadening, the loop 237ul is inserted between the column and the detector. Then compare to the separation result when the loop was not inserted with the same flowrate. 0.8 mL/min

The retention time of uracil, benzene and toluene are increased, the peak widths are wider significantly.
The retention times changed a little due to extra column band broadening. The peaks appeared to be wider are asymmetric and the intensity also changed. Therefore the retention times is not the same as previous ones.
9. Injection volume and peak compression
Injection loop 20ul
Sample(uracil, benzene, toluene) is diluted 10 times by water, inject the sample no peak appears.

Table 4. Result with diluted sample with 20ul injection loop
Although there are 2 peaks but the signals are at low levels.
Next step, change to injection loop 200ul
Inject the diluted sample,
the result

Table 5. Result with diluted sample with 200ul injection loop
There are three peaks obtained.
If the sample is diluted 10 times(similarly to diluted with water), the peak of benzene and uracil is compressed. Peak compression means two or more peaks are overlapping. One peak appeared include many peaks with variable heights from different sample components .
Table 6. Result with diluted sample by MeOH with 200 injection loop.
Compare the band broadening: When a more polar solvent was used to dilute the sample, the width of peaks are much large than the diluted sample by water. Because the components in the sample diluted with MeOH will have high diffusion coefficient in the polar mobile phase in which fraction of MeOH defines the polarity of the mobile phase.
Peak asymmetry factor: the peaks obtained when the sample is diluted by water is more balanced(peak asymmetry factor nearly ~1), otherwise the peaks obtained when MeOH is the solvent are not balanced(peak asymmetry factor 0,741 and 0,231 is much lower than 1).
For the peak of toluene, it is fronting. This can be explained as high diffusion coefficient of toluene before coming to the column, and its interactions with stationary phase.(have a look at HPLC troubling here)

Table 6. Compare peak asymmetry factor and band broadening of two solvents.
In analytical determinations, minimized the connection tubes in the Chromatographic system, sample should be more polar or less, that is dependent on the polarity of the sample.










No comments:
Post a Comment
Bạn cần thêm thông tin hay có câu hỏi vui lòng comment